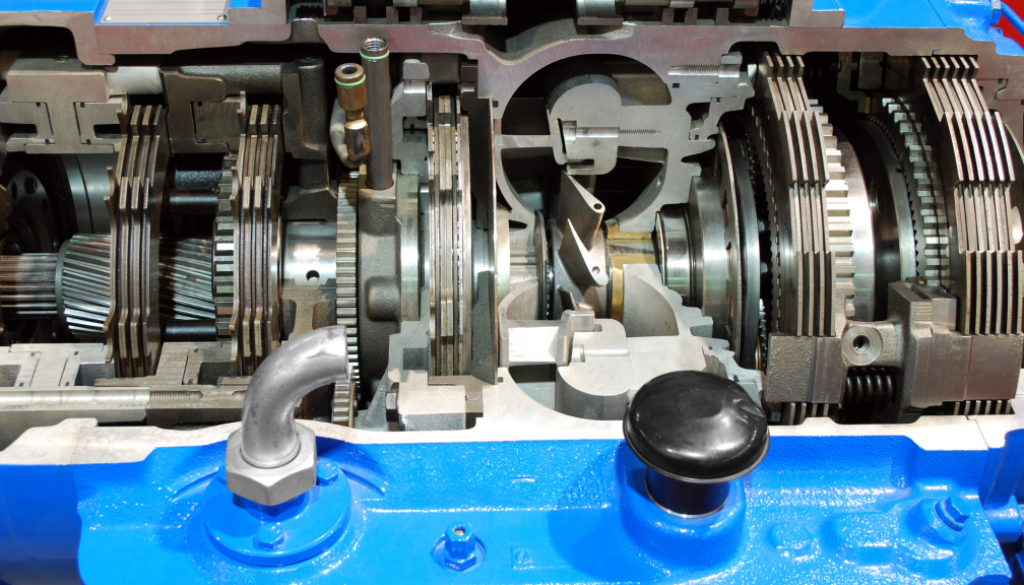
A truck’s transmission is one of the most critical components in ensuring smooth operation and durability on the road. When your transmission starts acting up, it’s not just an inconvenience—it’s a potential roadblock to your work and safety. Whether you’re managing a fleet or driving a single truck, understanding how your transmission works and knowing the signs of trouble can save you from costly breakdowns and repairs.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of truck transmission repairs, provide real-world examples, and explain what you can do to keep your transmission in top shape.
What Does a Truck Transmission Do?
The transmission in your truck transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing you to shift gears and control your speed. There are two main types of transmissions:
- Manual Transmissions: Require the driver to manually shift gears using a clutch and gear stick. These are often preferred for heavy-duty trucks due to their durability and efficiency.
- Automatic Transmissions: Handle gear changes electronically, offering smoother shifts and ease of use.
Without a properly functioning transmission, your truck can’t transfer power effectively, leading to performance issues, reduced fuel efficiency, and potentially complete breakdowns.
Signs of Transmission Problems
Catching transmission issues early is critical. Here are some common warning signs to watch for:
Difficulty Shifting Gears
If you’re struggling to shift gears or notice hesitation, it could indicate problems with the clutch, linkage, or internal transmission components.
Strange Noises
Grinding, whining, or clunking noises when shifting or driving often point to worn gears, a failing torque converter, or low transmission fluid.
Fluid Leaks
Transmission fluid is vital for keeping the system cool and lubricated. If you notice red or brown fluid pooling under your truck, it’s time to investigate.
Slipping Gears
When your truck unexpectedly shifts out of gear or struggles to stay in gear, it’s often a sign of internal wear or fluid issues.
Burning Smell
A burning odor could mean your transmission is overheating, often caused by low fluid levels or excessive friction.
Diagnosing Transmission Problems
When it comes to diagnosing transmission issues, a systematic approach is key. Here’s what professionals look for:
Visual Inspection
- Check for fluid leaks around the transmission housing.
- Inspect the condition of the fluid. Clean transmission fluid is typically red and smells slightly sweet. If it’s dark or smells burnt, it’s a sign of trouble.
- Look for worn or damaged components in the clutch or linkage system (for manual transmissions).
Using Diagnostic Tools
Modern trucks often come equipped with onboard diagnostic systems (OBD-II). Mechanics use scanners to read error codes that can pinpoint specific issues, such as solenoid failures or sensor malfunctions.
Test Drive
A test drive allows mechanics to identify irregularities, such as hesitation, slipping, or strange noises during shifts. This step provides critical clues about what’s happening inside the transmission.
Common Truck Transmission Repairs
Transmission repairs can range from simple fixes to extensive overhauls. Here are some common types of repairs and what they involve:
Fluid Replacement or Flush
Over time, transmission fluid degrades or becomes contaminated. A flush or fluid replacement is often the first step in resolving minor issues and preventing major damage.
Clutch Repairs (Manual Transmissions)
Clutches wear out over time, especially in trucks that frequently haul heavy loads. Replacing the clutch disc, pressure plate, and release bearing is a common repair.
Solenoid Replacement
Transmission solenoids control the flow of fluid through the system. When they fail, you might experience erratic shifting or stuck gears. Replacing faulty solenoids restores smooth operation.
Valve Body Repairs
The valve body controls the flow of transmission fluid. If it becomes damaged or clogged, it can cause shifting problems. Repairs often involve cleaning or replacing specific components.
Rebuilding or Replacing the Transmission
In severe cases, such as extensive internal wear or damage, the transmission may need to be rebuilt or replaced entirely.
Tools and Technology Used in Transmission Repairs
Transmission repairs often require specialized tools and equipment. Here are some examples:
- OBD-II Scanners: Diagnose error codes and pinpoint specific problems.
- Transmission Jacks: Safely remove and install heavy transmission units.
- Pressure Testers: Measure fluid pressure within the system to identify leaks or blockages.
- Torque Wrenches: Ensure bolts and fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Digital Fluid Gauges: Provide precise readings of fluid levels and temperature.
Conclusion
Your truck’s transmission is vital to its performance and reliability. By staying alert to warning signs, maintaining proper fluid levels, and addressing small issues early, you can extend the life of your transmission and avoid costly repairs. Adding preventative habits like routine checks and seasonal adjustments ensures your truck remains reliable in any condition.
If you ever face a transmission problem you’re unsure about, don’t hesitate to consult an experienced mechanic who can get to the root of the issue. Addressing the problem sooner rather than later can save you time, money, and stress.